Business Analyst Role in Testing / BA in testing
Let us discuss here what is Business Analyst Role in Testing

Business Analyst Role in Testing / BA in testing
As I mentioned in the main page, in a software company there will be Testing team. In industry terms we call it as Quality Assurance (QA) team or Quality Control (QC) team. Most popular terminology is QA or testing. Let us try to understand what is Business Analyst role in Testing.
My intention of putting ‘testing’ knowledge here is to make Business Analyst aspirants to know about testing not intended for Developers and testers. As a Business Analyst it is important to know how testing is done and how testers perform in real life scenarios. Let’s see now, how and what a ‘tester’ will do in real time projects;
First let us understand why testing team is needed in Software Company or software project or why team needs to test the software application or product?
“Testing” will not applicable only for software product or application. “Testing” is applicable everywhere in our day to day life also. For example, before buying clothes we will test whether these clothes will suit to us or not.
Another example: Before buying two wheeler or four wheeler we will test the vehicle whether it will suit to us or not and all the functionalities are working or not.
Similarly testing team will test the software product/ application before releasing to client or market. Without proper testing we will not find quality product. If testing not done properly then software will have so many problems or issues. It leads to project failure, because no one will accept application with issues or problems.
So testing is very important during the project execution.
In ‘Testing’ there are 2 major types
a) Black-box testing
B) White-box testing
Sample BA Document Templates
FREE DOWNLOAD |
Black-box testing: Let me put in simple words, black-box testing deals mainly with the functionality testing. Here we test – if ‘x’ is input, are we getting ‘y’ as output.
White-box testing:
here also tester will test if ‘x’ is input ‘y’ is the output or not but this type of testing deals with technical things. How program logic is written? Based on the code is the input and output are proper or not? How input is interacting with backend database and how results are fetched.
In simple words you can say, black-box testing needs functional knowledge and white-box needs technical knowledge.
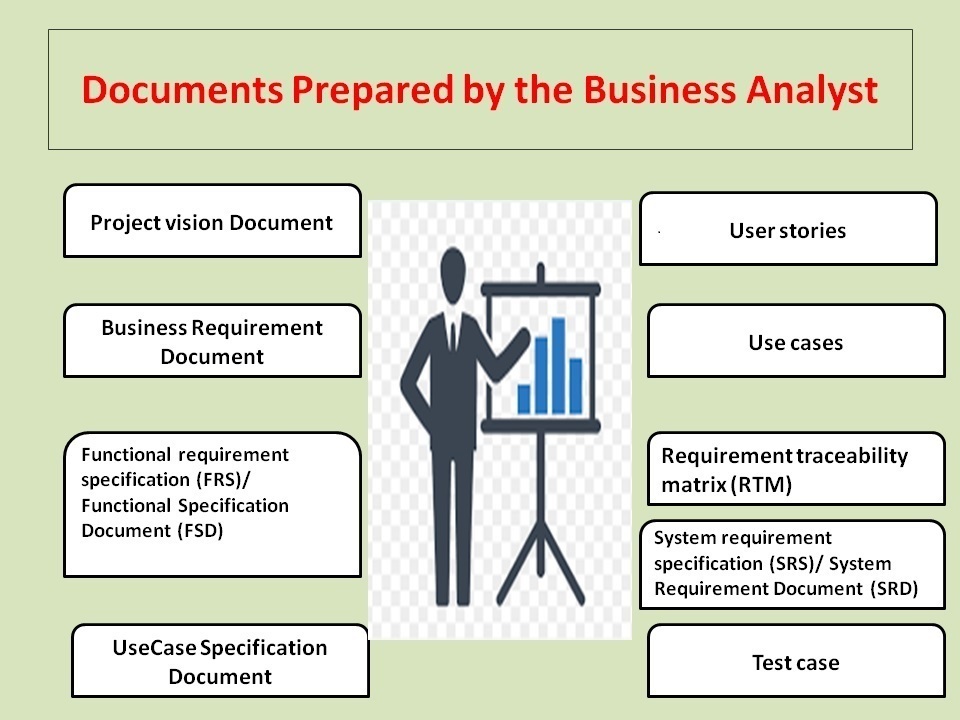
As you know, Business Analyst will do Business requirements gathering and prepare SRS/FSD/FRS and share the documents with Development and testing team. Testers will read the SRS /FSD/FRS and if any doubts are there then they will ask Business Analyst for clarifications. Then Business Analyst will clarify all the doubts and arrange meetings if needed. After all the clarifications are made as first step; ‘Testing Lead’ will create high level Test Scenarios. In the test Scenario it will be mentioned – what to be tested? What all modules are to be tested and what all are the high-level expected results?
Testers will write Test-cases which will be based on the SRS /FSD/ FRS document provided by Business Analyst. Test cases will be written in detail for each field and each function.
For entire application and including all the modules ‘test cases’ will be written. Usually MS-Excel will be used to write test-cases. Once test cases are ready then a senior tester or any of the other testers will review the test-cases.
Once Developers code the functionality build will be passed to testing team. (What is Build? – Build is the terminology used. Build means – Developed code.) Build will be tested in phase wise and accordingly to test plan prepared by Testing team leader. Testing will be done based on the test cases written. Usually it is called “test-case” execution. Before testing team start testing there are some tests.
Before build is passed to testers there are some testing done. Yes!! Developers themselves do a round of testing before passing build to testing team. We call it as “Unit Testing”. Developers will write Unit Test- cases and execute unit test cases.
After unit testing is done, there is one more testing called BVT (build Verification testing). This testing is done by developers or testers or deployment engineer. The main purpose of this test is to ensure the Build is stable or not. (note: there will be different servers like development or lab server, test server, production server) when build is deployed in different server all the path and connections need to be changed and build should be ensured working. If not working Testers will not be able to test build. Also if any major bugs (what is Bug: it is terminology again. Bug means mistake or error) testing team will reject the build form testing.
After BVT is done testers will start testing the build as per test-cases written. Any bugs found will be logged into central repository. There are some tools specifically for testing team which will act as repository and as well as tracking purpose. Any bugs can be logged into tool and assign to development team. An email will be triggered to developer on that bug. Developer will check and if it is a bug he will fix that bug. If not bug developer will write his comments for that bug and close the bugs]
When testers log bugs and it will be fixed by developers, again it will be tested. The fixed functionality will be tested – this is called “Patch testing”. Usually any patch or fixes done by developers will have impact on different functionality so again from start application need to be tested. This type of testing is called “Regression Testing”
The other testing types are;
Smoke testing: This is a sort of high level testing done on all the major functionality to ensure all the main parts of software are working. This does not do in-depth testing minute level.
Sample BA Document Templates
FREE DOWNLOAD |
Sanity testing:
This is to ensure all parts of software are working but this testing focuses on minute level of functionality.
Integration Testing:
Software will be developed in phases or modules. Each module developed will be tested separately and at the end all the modules will be clubbed and tested. This is called Integration testing.
System testing:
This is to ensure entire software is working properly. In this test not only testers but business analysts, consultants and other people will test. This is something like preparatory exam before main exam. After system testing is done build will be deployed for UAT.
UAT:
User Acceptance testing – this is done by clients.
Beta Testing: This is done by both client and testing team or business analyst. Once UAT is passed and application is deployed for usability for some period application will be on Beta.
Now lets see bug classification:
- Blocker bugs
- Major bugs
- Critical bugs
- Normal bugs
- Trivial bugs
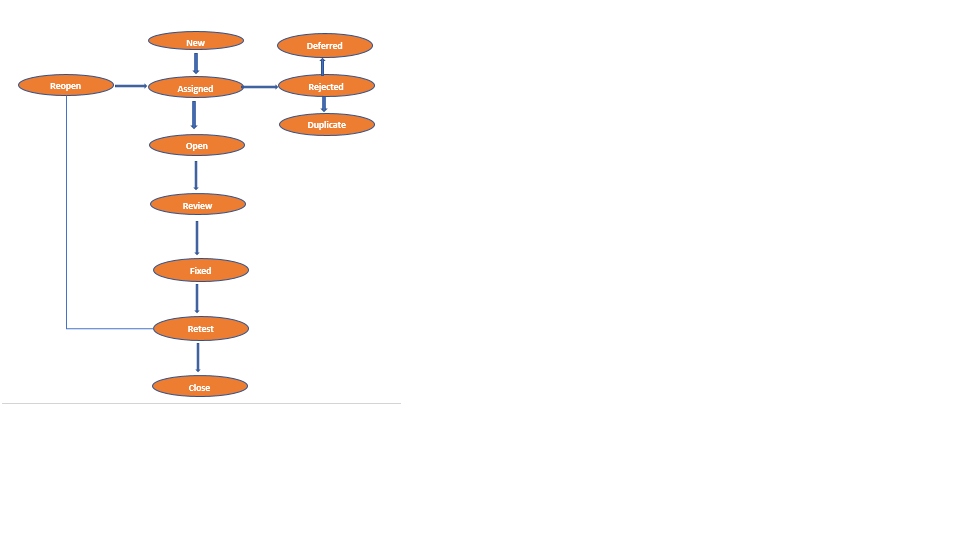
Defect or Bug Life Cycle
Blocker Bugs are those which blocks testers from further testing, say for example if application is having Login function and after login testers are supposed test some functions BUT if they are not able to login. i,e. some problem in development with respect to login function we call it as Blocker bug.
other important bugs which are critical will be categorized into major and critical.
Some small bugs like not accepting numbers, telephone number is accepting alphabets are considered as normal and trival bugs.
Once bugs are raised testers will pass it to developers, once developers fix those bugs it will be passed back to testers for verification of fixed bugs. if again there is some problem with fixed bugs testers will pass it back to developers. This cycle repeats and once bug is fixed, testers will verify and close the bugs.
There are some open source tools like Bugzilla which are used to keep track of bug status. i.e. opened, closed, verified etc..
Also there are 2 more types of bugs called Invalid bugs and duplicate bugs. If testers raise some bugs which have no problems then developers will mark it as Invalid bugs. If same bugs are repeated then developers will mark it as Duplicate bugs.
(Note Again: this article is for Business Analysts and not for testers because for testers testing document need to be in depth. This is just for understanding QA or testing cycle).
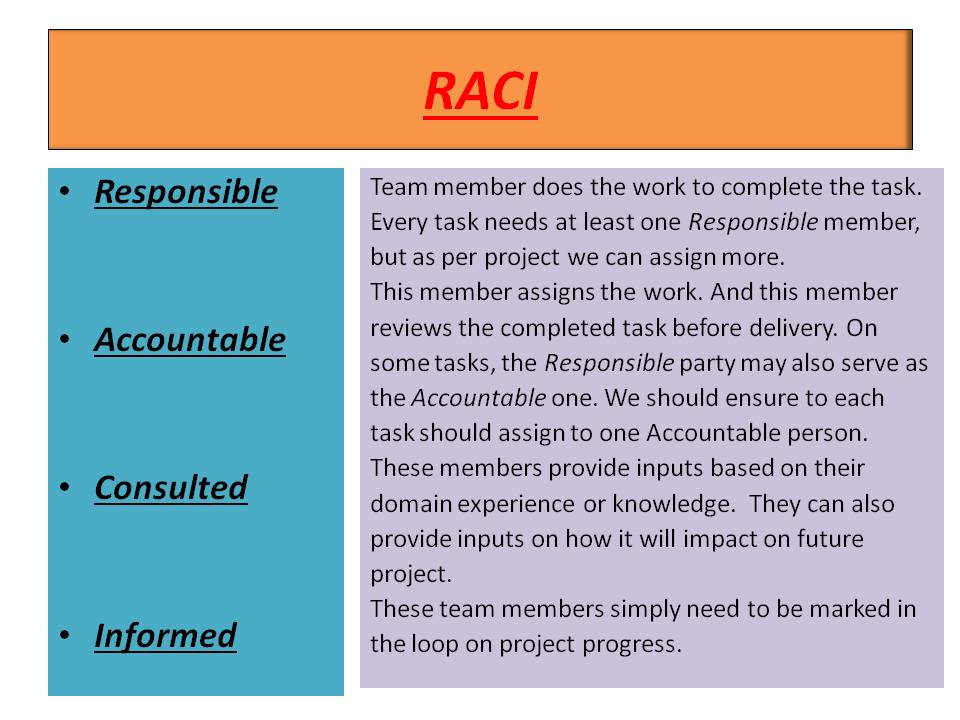
Business Analyst involves in Testing phase, so it is good to have knowledge on testing.
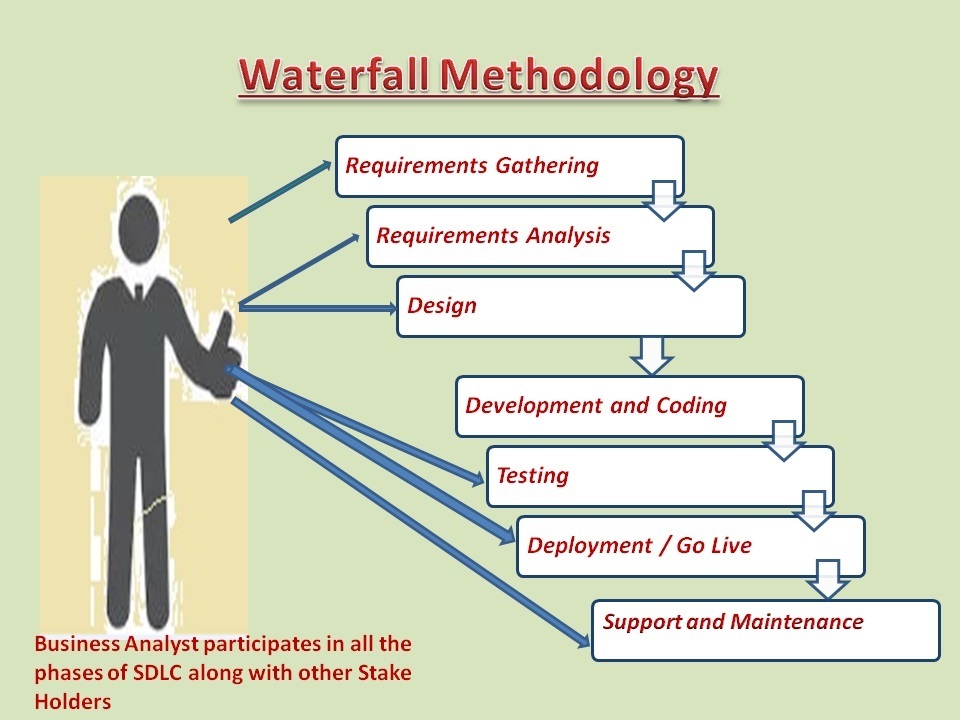
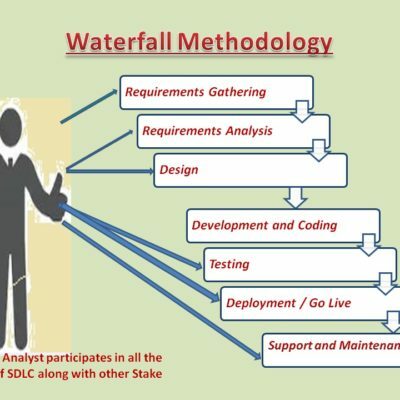
Depends on the organization Business Analyst participates in all the phases of SDLC except Development.
It does not mean that Business Analyst will not participate in development phase, Business analyst explains the requirements to development team if team needs more clarity on the requirements.
I hope this article helped you to understand what is Business Analyst role in testing
Sample BA Document Templates
FREE DOWNLOAD |
FAQS: Testing and UAT
What is the business analyst role in UAT?
The Business Analyst Role is central to achieving success in UAT sessions. … UAT helps stakeholders to determine whether the system can be put to use in real-life business scenarios or not. 2. The UAT session is an opportunity for users to see the solution in action and confirm that it meets their needs.
Who writes UAT test cases?
When it comes to UAT, often the UAT is composed of Business Analysts and selected end-users who will perform the actual UA testing. But QA, who have an overall responsibility to ensure the application/product works as required, should be part of the process for test definition
Who is responsible for UAT?
In summary, quality assurance is the responsibility of the business user and it therefore Party R responsible for executing the UAT. While a project manager (Party D) can help facilitate the time line and sign off process, and should support and be accountable for getting it done with Party R responsible for UAT.
Who runs UAT?
For many, UAT belongs in the hands of business analysts and corresponding business owners. These individuals collaborate to create the test plans and test cases and then determine how to implement and track their progress, all the while integrating the skills of technical experts and a quality assurance team.
Is UAT functional testing?
User Acceptance Testing (UAT) is a type of testing performed by the end user or the client to verify/accept the software system before moving the software application to the production environment. UAT is done in the final phase of testing after functional, integration and system testing is done.
Why is UAT important?
UAT is important because it helps demonstrate that required business functions are operating in a manner suited to real-world circumstances and usage. Verified and tested by the people who are going to be working with it on a daily basis. Basically you and your team are getting a better piece of software
What is UAT sign off?
UAT Sign–off: When all defects are resolved, the UAT team formally accepts (or recommends acceptance to the project manager) the software application as developed. The approval shows that the application meets user requirements and is deployable.

Business Analyst , Functional Consultant, Provide Training on Business Analysis and SDLC Methodologies.
🌐 Founder of BACareers.in| Freelance Business Analyst & Content Writer | Banking Domain Expert | Agile Practitioner | Career Mentor
I am the founder and content creator of BACareers.in, a specialized platform for aspiring and experienced Business Analysts. I share real-world insights, career tips, certification guidance, interview prep, tutorials, and case studies to help professionals grow in the BA career path.
We have strong experience in Banking, Financial Services, and IT. We bring deep domain knowledge and hands-on expertise in core banking systems, payment integrations, loan management, regulatory compliance (KYC/AML), and digital banking transformations.
💼 Business Analyst Expertise
Requirement Elicitation, BRD/FRD, SRS, User Stories, RTM
Agile & Waterfall (Scrum, Kanban) methodologies
Business Process Modeling (BPMN, UML, AS-IS/TO-BE)
Stakeholder Communication & Gap Analysis
UAT Planning, Execution & Support
Core Banking Solutions (Finacle, Newgen BPM, Profile CBS, WebCSR)
✍️ Content Writing & Strategy
Founder of BACareers.in – knowledge hub for BAs & IT professionals
SEO-optimized blogs, training content, case studies & tutorials
Content on Business Analysis, Agile, Banking, IT & Digital Transformation
Engaging, beginner-friendly writing for professionals & learners
🌍 What we Offer
Freelance Business Analysis services: BRD, FRD, UAT, process flows, consulting
Freelance Content Writing: SEO blogs, IT/business content, case studies, LinkedIn posts
A unique blend of analytical expertise + content strategy to turn business needs into solutions and ideas into words that work
📌 Whether you’re an organization seeking BA expertise or a platform needing impactful content, let’s connect and collaborate.
Business Analyst, Agile, BRD, FRD, Banking, Content Writer, SEO writing.