Data Mapping
Data beats feelings. Still, data also causes feelings. Especially negative feelings if your data does not give any practicable perceptivity on the subject. Data mapping and its indecorous perpetration are the most significant reasons behind point less insights. The lack of unified criteria and naming conventions across different data sources makes it hard for judges to see a holistic picture of business conditioning and make data- driven opinions. Without formalized perceptivity and multitudinous data disagreement all the time spent on data aggregation may be wasted in vain. This problem most explosively manifests itself in digital advertising, where different marketing tools have different names for the same metric. Ultimately, companies can’t find an operation to their data.
A recent study by Inc plant that over to 73 of company data goes unused for analytics. In this post, you’ll learn what data mapping is, how it solves data analytics issues, and what data mapping tools help non-technical judges gain demitasse clear insights.
As a Business Analyst, what is data and what are the fields in old system and New System for migration projects.
What is data mapping?
Data mapping is a process of matching fields from different datasets into a schema. The data mapping process identifies the target (for illustration, data storehouse table) data element for each source element (for illustration, transactional system).
Data mapping is the first step for a variety of different tasks, similar as Data migration Data transformation Data ingestion Merging of multiple datasets or databases into a single database. While moving information from one source to another, data specialists have to ensure that the meaning of information remains the same and applicable for the final destination.
In other words, data mapping helps databases talk to each other. Let’s consider the illustration of marketing metrics. Marketers frequently need to gather information from Google Analytics and Google Search Console in one place. These tools keep information about new druggies coming from Google in their own database. However, you’ll have to count the same caller doubly, If you just combine data from both sources. That’s why you need to produce a data chart that connects Google sessions in Google Analytics and clicks from Google Search Console. In this way, you can avoid duplications and fill your new database with precise data.
How to do data mapping?
To understand how data mapping works, we first have to figure out what data models are. A data model is an abstract model that describes data rudiments are arranged and how they relate to each other and other entities. Here are some of the most common data models Since there is no unified way to organize data in different models, data fields in two separate datasets might have distinct structures. But why do we need to know the way data is arranged in databases and how different datasets relate to each other?
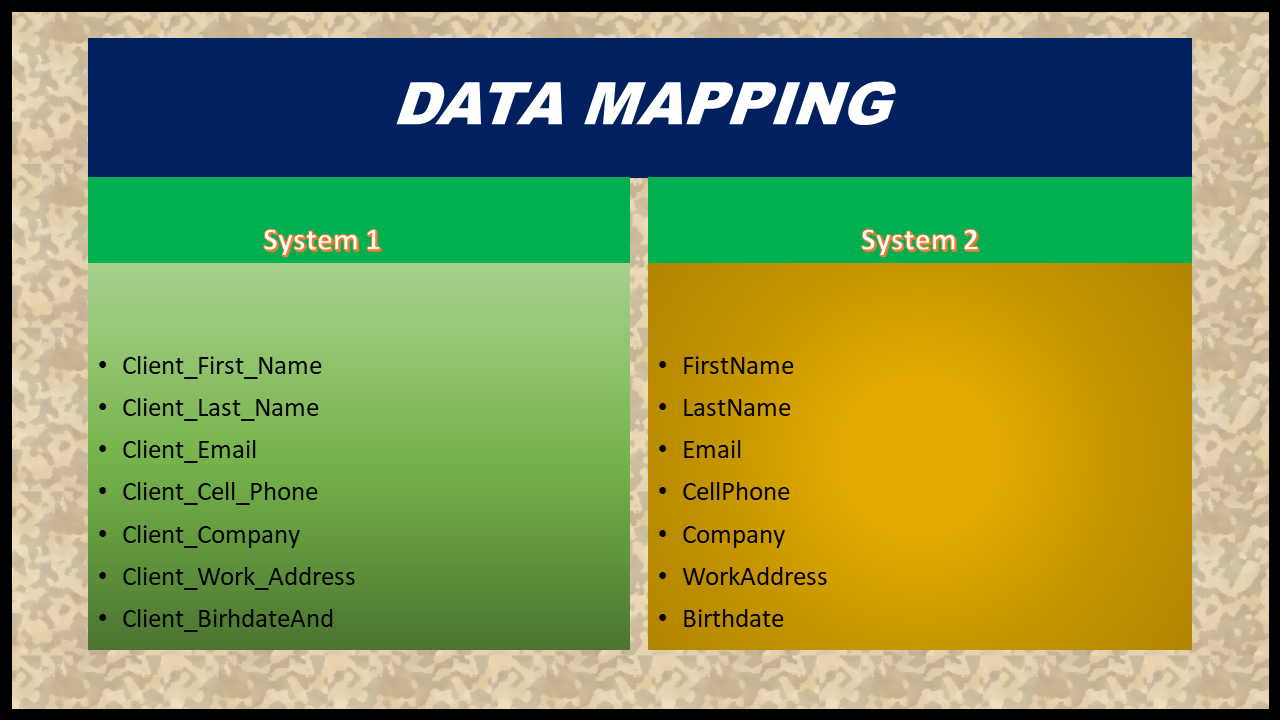
Imagine that your company used a particular CRM system for a long time, but now it can’t manage with your requirements, and the company migrates to another solution. Likely, your new system habit have the same data format as your old bone. The new system might contain new data fields, naming conventions, and fields order.
While the former result stored data in the following format Client_First_Name, Client_Last_Name, Client_Email, Client_Cell_Phone, Client_Company,Client_Work_Address,Client_BirhdateAnd your new result might have the following data formatting Last Name, First Name, Company, Work Address, Cell Phone, Birthdate, Email.
As you can see, these results have different data structures and naming conventions. In this case, copy pasting information would do no good. That’s where data mapping comes to help. With the help of a data chart, you can produce a set of rules which will make the data migration smooth and successful.
Here’s how data mapping between two CRMs works. These rules govern the data migration workflow in the following way.
Take the data from the first field of the old CRMs database and put it into the alternate field of the new CRM’s database.
Take the data from the alternate field of the old CRMs database and put it into the first field of the new CRM’s database. And so on Of course, these rules should also consider variables data types, the size of the data field, Â data fields names, and other details. But this illustration gives a high- position understanding of how data mapping works in mortal terms.
Data mapping advantages
The major advantage of data mapping is egregious judges get well-structured, analysis-ready data in the asked destination by mapping out your data. But what it gives you on a grander scale, and how it benefits your business? Let’s find out.
Three crucial benefits of data mapping tools Common data language. With data mapping, businesses achieve a grainy of their performance. Let’s take marketing platforms as an illustration. Every marketing platform has its own picking conventions for the same metric. Hence, every platform calls the same metric in different ways. Impressions, views, imps, imp are different names for the same criteria used by different tools.
Analysts can unify criteria from colorful sources to aggregate them in a single marketing report with data mapping. That’s how marketers can get a holistic view of the crusade performance and make the right opinions faster. This use case also applies to deals brigades, reclamation brigades, and other departments that use numerous data sources in their day-to- daywork. Recommendation systems Data mapping is one of the crucial factors behind behavior are targeting.
 Businesses similar as Amazon excerpt precious perceptivity from druggies browsing habits, purchase history, time spent on a runner, viewing history, and other data. Then, data specialists connect these perceptivities with other stats similar as demographic information or druggies purchase power.
By combining data from these sources, Amazon can target druggies with certain products and epitomize shopping gests grounded on a number of factors (e.g., challenges guests may be facing, their position, age, interests, education, occupation, and numerous further).
Still, to get the real value out of plain information, data experts must invest considerable sweats in data mapping because of data heterogeneity. Lead attribution Companies can track where their prospects come from and what marketing channels are the most effective by making your perceptivity talk to each other. With data mapping, marketers align criteria from different sources and combine them together. With data from analytics platforms similar as Google Analytics or Mixpanel and data from CRM systems similar as Hubspot or Shopify advertisers identify which data should be credited for each conversion. This data- driven criterion model gives a more accurate view of marketing performance and allows for better allocation of advertising budget.
Let us discuss the tools in next article.

Business Analyst , Functional Consultant, Provide Training on Business Analysis and SDLC Methodologies.