Introduction
In traditional Agile frameworks, the term Scrum BA refers to a Business Analyst working in a Scrum environment. While the Scrum Guide does not officially define a Business Analyst role, in real-world projects, BAs play a critical part in ensuring that requirements are clear, business goals are met, and products deliver value to stakeholders.
In this article, we’ll explore what ScrumBA means, the BA’s role in a Scrum Team, and how they add value throughout the Agile lifecycle—with real-time examples and practical scenarios.

What is ScrumBA?
ScrumBA is a term used to describe a Business Analyst who works within a Scrum team. These BAs adapt to Agile values and practices and collaborate with Product Owners, Scrum Masters, and Development Teams to deliver high-value increments in each sprint.
While not an official Scrum role, ScrumBAs are crucial in bridging the gap between business and technology.
Scrum Roles Recap
Before understanding ScrumBA, let’s quickly review the standard Scrum roles:
Product Owner (PO): Owns the product backlog and defines what to build.
Scrum Master (SM): Facilitates the Scrum process and removes impediments.
Development Team: Builds the product increment.
To read more about Scrum roles, visit:
👉 Scrum Roles Explained with Real Examples
Where Does the BA Fit in Scrum?
Although the Scrum Guide doesn’t list BA as a formal role, the Business Analyst can play a supportive and collaborative role, particularly in:
Backlog refinement
Writing user stories and acceptance criteria
Understanding and communicating business needs
Supporting the Product Owner
Ensuring stakeholder alignment
Responsibilities of a ScrumBA
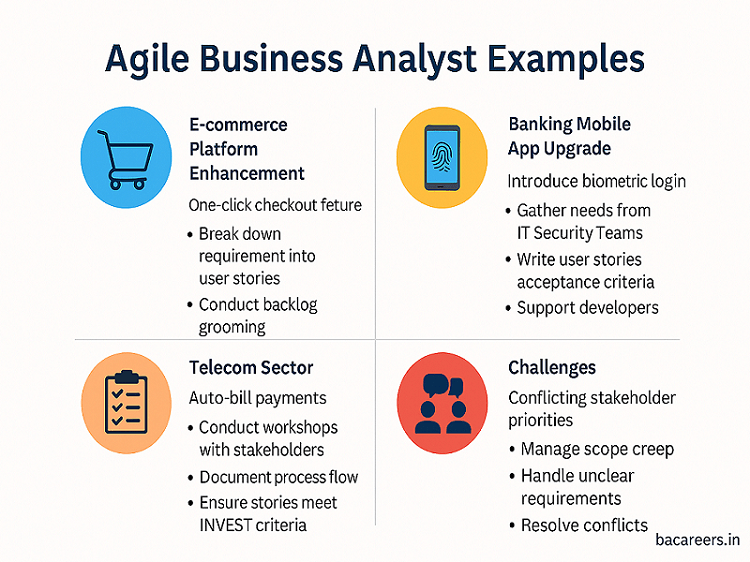
1. Support Product Owner in Backlog Management
ScrumBAs help refine backlog items, split epics into stories, and ensure clear acceptance criteria are defined.
✅ Example:
In a digital banking project, the PO provides an epic: “Enable Mobile Loan Applications.”
The ScrumBA works with stakeholders to split it into clear stories:
“Submit KYC through mobile”
“Track loan approval status”
“Upload income documents”
2. Gather & Clarify Requirements
ScrumBAs bridge communication between business stakeholders and the Scrum Team, helping to avoid misinterpretations.
✅ Real-Time Scenario:
In an e-commerce app, users report confusion about coupon codes. The ScrumBA interviews users and discovers the need for a clearer UX flow and success messages. These insights are translated into actionable stories.
3. Define Acceptance Criteria
They write clear and testable acceptance criteria to ensure deliverables match expectations.
✅ Example:
For the story “Apply Coupon at Checkout,” a ScrumBA writes:
Given the user is on the checkout page
When they enter a valid coupon
Then a discount should be applied to the total price
4. Facilitate Communication Between Stakeholders & Team
ScrumBAs ensure that feedback loops are quick and aligned with sprint goals.
✅ Real-Time Scenario:
In a healthcare app, a BA collects feedback from doctors and translates it into user stories for the development team, improving usability for the “Appointment Scheduling” feature.
5. Support Sprint Planning and Reviews
ScrumBAs provide business context during sprint planning and help demonstrate user stories during sprint reviews.
✅ Example:
During Sprint Review for a loyalty program, the ScrumBA walks through how a new reward points system aligns with customer retention goals.
ScrumBA vs Traditional BA
| Aspect | Traditional BA | ScrumBA |
|---|---|---|
| Documentation | Detailed upfront BRD/FRD | Lean documentation, evolving stories |
| Communication Style | Formal and structured | Collaborative and iterative |
| Engagement with Team | Works with business separately | Part of the Scrum Team |
| Tools | Excel, Word, Visio | JIRA, Confluence, Miro |
To explore more differences, read:
👉 BRD vs FRD – What’s the Difference?
Tools That ScrumBAs Use
JIRA / Azure DevOps – For user story tracking and backlog management
Confluence – For knowledge sharing and documentation
Miro / Lucidchart – For visual workflows, process diagrams
SQL / Excel – For data analysis when needed
Common Challenges Faced by ScrumBAs
| Challenge | How ScrumBA Helps |
|---|---|
| Vague requirements | Clarifies scope through story mapping sessions |
| Frequent changes in priorities | Works with PO to re-prioritize based on value |
| Miscommunication with dev team | Clarifies business context and acceptance criteria |
Benefits of Having a ScrumBA in Agile Teams
✅ Improved requirement clarity
✅ Faster feedback loop
✅ Better stakeholder collaboration
✅ Increased sprint success rate
✅ Smooth UAT planning and sign-off
Conclusion
While not officially defined, the ScrumBA is a powerful enabler in Agile environments. They ensure business goals are clearly translated into actionable, testable, and valuable stories for the Scrum team.
As Agile adoption grows, ScrumBAs are becoming an essential part of modern product teams, especially in industries like banking, healthcare, retail, and fintech.
Related Articles on BACareers:
External Resources

Business Analyst , Functional Consultant, Provide Training on Business Analysis and SDLC Methodologies.
🌐 Founder of BACareers.in| Freelance Business Analyst & Content Writer | Banking Domain Expert | Agile Practitioner | Career Mentor
I am the founder and content creator of BACareers.in, a specialized platform for aspiring and experienced Business Analysts. I share real-world insights, career tips, certification guidance, interview prep, tutorials, and case studies to help professionals grow in the BA career path.
We have strong experience in Banking, Financial Services, and IT. We bring deep domain knowledge and hands-on expertise in core banking systems, payment integrations, loan management, regulatory compliance (KYC/AML), and digital banking transformations.
💼 Business Analyst Expertise
Requirement Elicitation, BRD/FRD, SRS, User Stories, RTM
Agile & Waterfall (Scrum, Kanban) methodologies
Business Process Modeling (BPMN, UML, AS-IS/TO-BE)
Stakeholder Communication & Gap Analysis
UAT Planning, Execution & Support
Core Banking Solutions (Finacle, Newgen BPM, Profile CBS, WebCSR)
✍️ Content Writing & Strategy
Founder of BACareers.in – knowledge hub for BAs & IT professionals
SEO-optimized blogs, training content, case studies & tutorials
Content on Business Analysis, Agile, Banking, IT & Digital Transformation
Engaging, beginner-friendly writing for professionals & learners
🌍 What we Offer
Freelance Business Analysis services: BRD, FRD, UAT, process flows, consulting
Freelance Content Writing: SEO blogs, IT/business content, case studies, LinkedIn posts
A unique blend of analytical expertise + content strategy to turn business needs into solutions and ideas into words that work
📌 Whether you’re an organization seeking BA expertise or a platform needing impactful content, let’s connect and collaborate.
Business Analyst, Agile, BRD, FRD, Banking, Content Writer, SEO writing.