Let us see here documents prepared by Business Analyst during the project. Business Analyst will prepare so many documents as per Company standards; here we will see what the documents are mostly created by the Business Analyst during the project life cycle.
These documents prepared by business analyst to fulfill the various project needs and cater to audiences belonging to different spheres of a project.
Documents prepared by Business Analyst
As we know Business Analyst primary and most important role is to gather the requirements, analyze the requirements and document the same with proper approvals, Business Analyst should ensure not to miss any requirement. For example, if any requirement is out of scope of the project and it is not feasible then Business Analyst needs to inform the same to stake holders prior to prepare the documents and get approvals from internal and external stake holders. If any requirement is out of scope or not feasible in this project then he needs to explain the scenarios and consequences and what problems we will face because of this requirement to internal and external stake holders. Business Analyst can update the same in meetings with stake holders and it should be documented in the form of FSD or FRD.
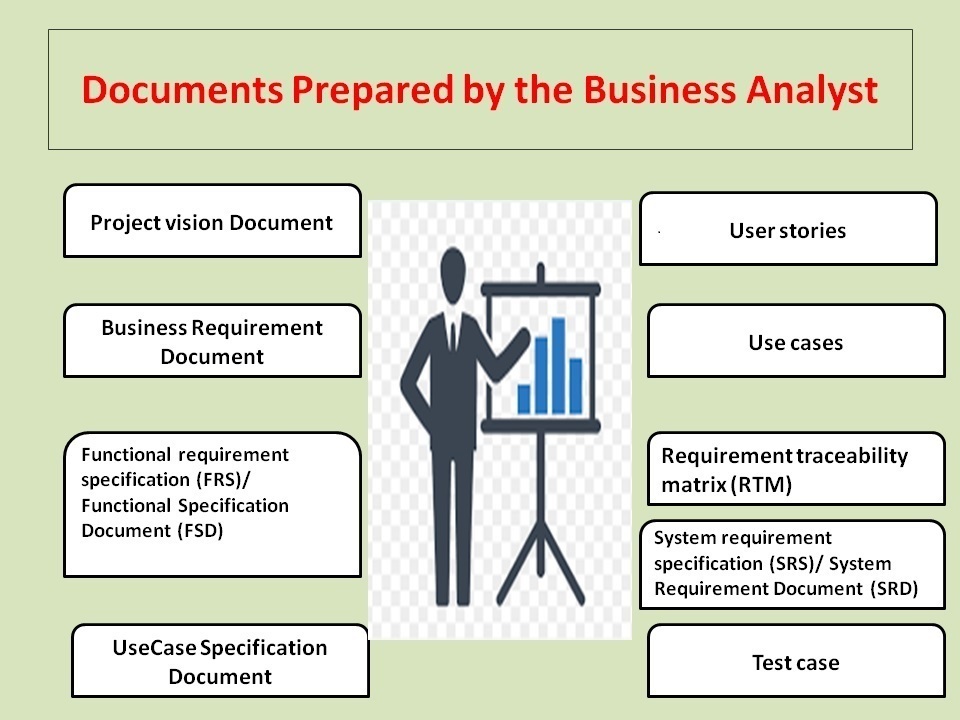
Documents Prepared by Business Analyst
The type and specifications a business analyst is expected to create in an organization depends upon many parameters like organization’s processes and policies, need and expectations of the business, and the stakeholder requirements. Detailed below are the common documents a business analyst is expected to created and they are extensively used throughout the project life cycle. Each of these documents has a specific template and it’s a part of the overall project documentation.
Let us observe what are the documents prepared by Business Analyst below
- Project vision Document
- Business Requirement Document
- Functional requirement specification (FRS)/ Functional Specification Document (FSD)
- User stories
- Use cases
- Requirement traceability matrix (RTM)
- System requirement specification (SRS)/ System Requirement Document (SRD)
- Test case
Project vision document: Project vision document will be prepared by client and project Manager, business analyst also expected to contribute to this document based on organization and project manager wish.
We will mention purpose of the product/software to be developed. We will describe what business objective will be achieved because of this product in high level.
The Project vision document contains: It may vary from organization to organization depends on organization and stake holders.
- Introduction
- Description of users in the system
- Project stakeholders
- Product Overview
- Product Features
- Product requirements
- Constraints/Limitations
- Quality/documentation requirements
Business Requirement Document (BRD)/ Business Requirement Specification Document. (BRS)
A Business Requirement Document is created to describe the business requirements of a product/process and the intended end result that is expected from the product/process. It is one of the most widely accepted project requirement document and is referred to throughout the development life-cycle for any project. A BRD mainly focuses on answering ‘what is the business solution’ as opposed to ‘how to achieve the business solution’ and thus it’s mainly centered around the business requirements. A BRD is created with the help of the project team (BA, client, subject matter experts, business partners) and is also used as a communication tool for other stakeholders/external service providers.
The Business Requirement Document contains:
- Document revision
- Approvals
- Introduction
- Business goals and objectives
- Stake holders
- Business rules
- Project background
- Project objective
- Project scope
- In-scope functionality (Requirements)
- Out-scope functionality (Requirements)
- Business requirements
- Data requirements
- Functional requirements
- Non_functional requirements
- Assumptions
- Constraints
- Risks
- Business process overview (modelling diagrams for instance, Use Case and Activity Diagram)
- Legacy systems
- Proposed recommendations
- List of acronyms
- Glossary of terms
- Related documents
- Dependencies of existing systems
Functional requirement specification (FRS)/ Functional Specification Document (FSD) Functional Requirement Document (FRD)
A Functional requirement specification or Functional Specification Document describes the intended behavior of a system including data, operations, input, output and the properties of the system.
In a BRD the requirements are high level but in an FRS/FSD, they are written in much more details to capture each and every aspect of a requirement. Thus a functional specification document becomes a more technical, accurate and descriptive requirement document. Owing to their technical nature, FRS/FSD are equally used by developers, testers and the business stakeholders of a project.
Functional requirement specification (FRS)/ Functional Specification Document (FSD) Functional Requirement Document (FRD) contains
- Introduction – It should contain Purpose, Scope, Background, References, Assumptions and constraints, Dependencies and document overview
- Methodology
- Functional Requirements
- Modeling Illustrations – Context, User Requirements, Data Flow Diagrams, Logical Data Model/Data Dictionary, Functional Requirements
- Other Requirements – Interface / Integration Requirements, Hardware/Software Requirements,
- Performance
- Glossary
- Requirements Confirmation
- Client Signoff (Client provide sign off on mail if client satisfies with the approach)
User stories:
In an agile development environment, a user story is a document describing the functionality a business system should provide and are written from the perspective of an end user/customer/client. The user stories are not very descriptive and only captures ‘who’, ‘what’ and ‘why’ of a requirement in limited detail. If any requirement is too big for a single user story it’s broken down into a number of user stories making it easier for estimation and discussion. In such cases, the main user story will act as an Epic (parent) user story.
Some examples of user stories are:
- The system shall be able to sort the values in ascending and descending order
- The application must allow the user to enter his name, date of birth and address.
- The system shall verify the login credentials of the user and redirect him to the dashboard in case of successful login.
Use cases
Each and every project is an endeavor to achieve ‘requirements’ and the document which defines these requirements is a use case. A use case is a methodology used in system analysis to identify, define and organize system requirements.
A use case is created from the perspective of a user and achieves the following objectives:
- Organizes the functional requirements,
- Iterative in nature and updated throughout the project life-cycle
- Records scenarios in which a user will interact with the system
- Defines other aspects like negative flows, UI elements, exceptions, etc..
The Use Case document contains:
- Actors
- Description
- Trigger
- Preconditions
- Normal Flow
- Alternative Flows
- Exceptions
- Special Requirements
- Assumptions
- Notes and Issues
Requirement traceability matrix (RTM)
A Requirement traceability matrix is used to record and track the relationship of the project requirements to the design, documentation, development, testing and release of the project/product. This is done by maintaining an excel sheet which lists the complete user and system requirements for the system (in form of use cases) which are in turn mapped to the respective documents like Functional Requirement, Design Document, Software Module, Test Case Number, etc.
An RTM is maintained throughout the lifecycle of the various releases in a project and it’s a vital document to track project scope, requirements and changes in any project.
The RTM Contains:
- Requirement ID
- Requirement Description
- Functional Requirement
- Status
- Architectural/Design Document
- Technical Specification
- Software Module
- Test Case Number
- Tested In
System requirement specification (SRS)/ System Requirement Document (SRD)
A detailed document containing information about ‘how’ the complete system has to function and enumerates hardware, software, functional and behavioral requirements of the system. This document elaborates the requirements from the perspective of observational behavior only and doesn’t consider technical or design bias.
The System requirement specification (SRS)/ System Requirement Document (SRD) contains:
- Product Perspective
- Product Functions
- User Characteristics
- General Constraints
- Assumptions and Dependencies
- External Interface Requirements
- Functional Requirements
- Classes / Objects
- Non-Functional Requirements
- Inverse Requirements
- Design Constraints
- Sequence Diagrams
- Data Flow Diagrams (DFD)
- State-Transition Diagrams (STD)
- Change Management Process
Test case
Although Business analysts are not explicitly asked to create test cases but they must understand what they constitute and how to create one, as they sometimes have to test functionalities by referring to the test cases.
A test case is a document, which has a set of test data, preconditions, variables and expected results created to verify and validate whether a particular piece of functionality is behaving as intended (or as documented in the requirement documentation). Thus, a test case becomes a standardized document which should be referred every time a requirement has to undergo testing.
Business Analyst will not prepare test cases but he sits with the QA team and ensure to all the requirements covered.
The components of a test case are:
- Test Case ID
- Test Scenario
- Prerequisite
- Test Data
- Test Steps
- Expected Results
- Actual Result
- Status
- Remarks
- Test Environment
All the above documents prepared by business analyst and are part of the project/product documentation. These documents are constantly referred through the project’s life-cycle for communication, reference and revision.
Templates may differ to organization to organization and project. Hope this article helped you to provide overview on what are the documents prepared by business analyst .
Sample BA Document Templates
Send download link to:

Business Analyst , Functional Consultant, Provide Training on Business Analysis and SDLC Methodologies.
