Introduction: Understanding the Role of Agile Business Analyst (BA)
Let us discuss in detail about Agile Business Analyst eamples ; In Agile environments, the Business Analyst (BA) plays a flexible and collaborative role—not traditionally defined like in Waterfall projects. Agile BAs bridge the gap between stakeholders and development teams, ensuring that business needs are effectively translated into working software solutions.
✅ Fact:
The International Institute of Business Analysis (IIBA) recognizes the importance of BA in Agile via its Agile Extension to the BABOK® Guide.
1. Who is an Agile Business Analyst?
An Agile BA is a professional who works closely with Product Owners (POs), Developers, and Stakeholders to deliver business value through iterative development cycles.
Core Activities Include:
Refining the Product Backlog
Writing User Stories
Eliciting requirements through collaboration
Assisting in Sprint Planning, Daily Stand-ups, Reviews, and Retrospectives
2. Real-Time Examples of Agile Business Analyst Responsibilities
Here are real-world examples to understand the daily activities of Agile BAs:
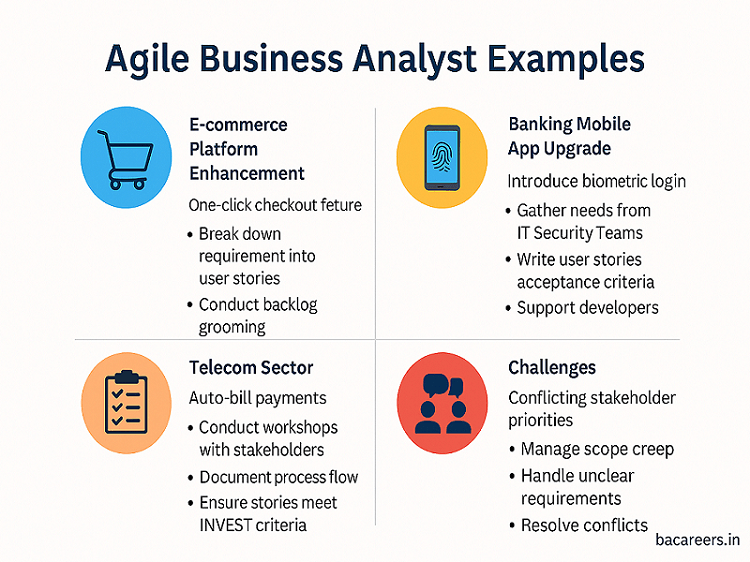
Example 1: E-commerce Platform Enhancement
✅ Scenario:
An e-commerce company wants to introduce a new feature: One-Click Checkout.
BA Role in Agile:
Collaborate with PO to break down the requirement into multiple user stories (e.g., Payment Gateway Integration, Security Checks, User Session Handling)
Conduct backlog grooming sessions with developers
Clarify functionality during Daily Scrum Meetings
Validate acceptance criteria during Sprint Reviews
Impact:
The feature reduced cart abandonment by 25% and improved customer retention.
Example 2: Banking Mobile App Upgrade
✅ Scenario:
A bank needs to introduce biometric login (fingerprint/face recognition) to improve security.
BA Responsibilities:
Interact with IT Security Teams to gather compliance needs
Write user stories with detailed acceptance criteria
Use Wireframes via tools like Miro or Figma to visualize user flow
Support Developers during Sprint execution
Result:
90% of users adopted the new login feature within 3 months.
3. Real-Time Scenario: BA in Action (Telecom Sector)
✅ Scenario:
A telecom company wants to implement Auto-Bill Payments for postpaid users.
BA’s Actions:
Conduct workshops with Finance, Legal, and Technical Teams
Identify potential risks (auto-payment failures)
Document process flow in Confluence
Use JIRA for maintaining User Stories
Ensure stories meet INVEST criteria (Independent, Negotiable, Valuable, Estimable, Small, Testable)
Outcome:
Auto-pay feature rollout improved on-time payments by 40%.
4. Key Skills Demonstrated by Agile BAs in These Examples
✔ Analytical Thinking — To decompose large features
✔ Collaborative Mindset — To coordinate between multiple stakeholders
✔ Technical Awareness — Understanding APIs, integrations
✔ Adaptability — Handling changing requirements
5. Tools Used by Agile Business Analysts
| Tool | Purpose |
|---|---|
| JIRA | Manage User Stories & Sprints |
| Confluence | Maintain Documentation |
| Miro/Figma | Create Wireframes & User Journeys |
| ChatGPT | Quick ideation & drafting |
6. Internal and External Links for Further Learning
🔗 Internal Links:
🌐 External Links:
7. Best Practices for Agile Business Analysts
✔ Focus on Value Delivery: Always prioritize high-value backlog items.
✔ Collaborate Closely: Work with POs, Devs, and Testers every Sprint.
✔ Embrace Change: Be open to evolving requirements.
✔ Document Visually: Use diagrams to simplify complex processes.
8. Challenges Faced by Agile BAs (with Examples)
| Challenge | Example |
|---|---|
| Scope Creep | Marketing team keeps changing feature expectations during Sprints. |
| Conflicting Stakeholder Priorities | Sales team vs. IT Security demands in Banking projects. |
| Unclear Requirements | In Telecom projects where 3rd party vendors are involved. |
Conclusion
The Agile Business Analyst is essential in delivering successful Agile projects. From refining backlogs to supporting sprint execution, BAs ensure that business value is consistently delivered, adapting to fast-changing environments.

Business Analyst , Functional Consultant, Provide Training on Business Analysis and SDLC Methodologies.
🌐 Founder of BACareers.in| Freelance Business Analyst & Content Writer | Banking Domain Expert | Agile Practitioner | Career Mentor
I am the founder and content creator of BACareers.in, a specialized platform for aspiring and experienced Business Analysts. I share real-world insights, career tips, certification guidance, interview prep, tutorials, and case studies to help professionals grow in the BA career path.
We have strong experience in Banking, Financial Services, and IT. We bring deep domain knowledge and hands-on expertise in core banking systems, payment integrations, loan management, regulatory compliance (KYC/AML), and digital banking transformations.
💼 Business Analyst Expertise
Requirement Elicitation, BRD/FRD, SRS, User Stories, RTM
Agile & Waterfall (Scrum, Kanban) methodologies
Business Process Modeling (BPMN, UML, AS-IS/TO-BE)
Stakeholder Communication & Gap Analysis
UAT Planning, Execution & Support
Core Banking Solutions (Finacle, Newgen BPM, Profile CBS, WebCSR)
✍️ Content Writing & Strategy
Founder of BACareers.in – knowledge hub for BAs & IT professionals
SEO-optimized blogs, training content, case studies & tutorials
Content on Business Analysis, Agile, Banking, IT & Digital Transformation
Engaging, beginner-friendly writing for professionals & learners
🌍 What we Offer
Freelance Business Analysis services: BRD, FRD, UAT, process flows, consulting
Freelance Content Writing: SEO blogs, IT/business content, case studies, LinkedIn posts
A unique blend of analytical expertise + content strategy to turn business needs into solutions and ideas into words that work
📌 Whether you’re an organization seeking BA expertise or a platform needing impactful content, let’s connect and collaborate.
Business Analyst, Agile, BRD, FRD, Banking, Content Writer, SEO writing.