BRD Document Vs FRD Document
Let us discuss BRD Vs FRD herre and how to to prepare the BRD and FRD.

Documentation is the most important aspect for any Business Analyst.
The documentation is useful to understand the requirements and the detailed discussion about new features and change request if any. Business Analyst will prepare many different types of documents. Some of the important ones are listed below –
- Business Requirement Document (BRD)
- User Stories
- Use Case Specification Document (USD)
- Functional Requirement Document (FRD)
- Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM)
- Product Requirements Document (PRD)
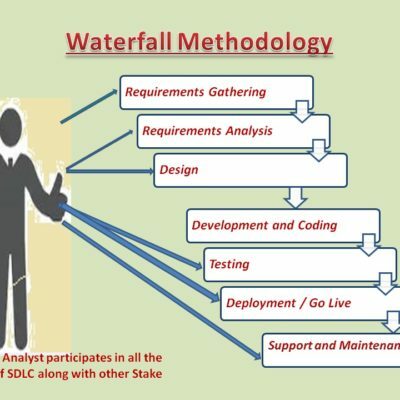
Documentation helps in understanding the business process and business events throughout the project. A Diagrammatically the documents can be pictured as a simple sheets of papers which contains some useful matter.
Let’s take a look at the similarities and differences between BRD and FRD.
Sample BA Document TemplatesSend download link to: |
Business Requirement Document
- BRD highlights “Business Requirements” – i.e., high-level business goals of the organization developing the product or solution with the help of IT.
- A formal document illustrating the requirement provided by the client
- In other words it describes at very high level the functional specifications of the software
- The requirements could be collected either by verbal or written or both
- Created by a Business Analyst who interacts with the client
- Entire work is executed under the supervision of the Project Manager
- It is derived from the client interaction and requirements
The BRD is important since it is the foundation for all subsequent project deliverable, describing what inputs and outputs are associated with each process function. It describes what the system would look like from a business perspective. Following are the most common objectives of BRD –
- To arrive at a consensus with stakeholders
- To provide input into the next phase of the project
- To explain how customer/business needs will be met with the solution
- Holistic approach to business needs with the help of strategy that will provide some value to the customer
Basically, stakeholder’s requirements can be small or big. Thus it needs to be break wherever it requires and should be taken as multiple requirements.
Format Of BRD –
There are many formats or templates that the organization follows. However, it depends upon the practices that is carried in the organization. For a product based company the BRD format is different as compared to service based firms. Standard format which is followed in most organizations are shown below. It is important to note that for clear understanding of the document we should include list of acronyms used.
The BRD template contains –
- document revision
- approvals
- introduction
- business goals
- business objectives
- business rules
- background
- project objective
- project scope
- in-scope functionality
- out-scope functionality
- assumptions
- constraints
- risks
- business process overview (modelling diagrams for instance, Use Case and Activity Diagram)
- legacy systems
- proposed recommendations
- business requirements
- list of acronyms
- glossary of terms
- related documents
Now let us look into FRD…
Sample BA Document TemplatesSend download link to: |
Functional Requirement Document
- FRD highlights “Functional Requirements” i.e., functionality of the software in detail
- Depending on the product.
- It will describes at a high level the functional and technical specification of the software
- Usually created by Business Analyst under the supervision of technical expert, for instance System Architect
- In a small and medium sized organizations a BA take care of this
- Few companies did not create FRD, instead they used BRD as it is detailed enough to be used as FRD as well
- FRD is derived from the BRD
- Will get sign off from the client once we prepare FRD
Actually, the process to reach the expectancy of the BRD is an FRD itself. Business Analyst will prepare the FRD after discussing with the stake holders and Project Manager. He is the person analyze the requirements, to get clarity on requirements he will conduct multiple meeting session with internal and external stake holders. And he will concentrate on below questions mostly.
- How we develop the expected requirement(s)?
- What are the tools and/or systems used and their dependencies?
- What are the features and functionalities?
- How will the customer reacts when they start using the solution?
- Any assumptions or constraints?
Most common objectives of FRD –
- Draw flow charts for each process flows for each activity interlinking dependencies
- Holistic view for each and every requirements, steps to built
- Estimating detailed risks for each new change request
- Highlight the consequences if the project health is weak to avoid scope creep
The FRD should document the operations and activities that a system must be able to perform.
Format Of FRD –
Likewise BRD, FRD has a somewhat different format focusing more on risks and interfaces. Although there is no such standard format that a Business Analyst should opt for. Companies belonging to different domains use their own template. For instance, you would find many points would be repeating as in BRD.
But there should be no confusion for BA to prepare this document.
The FRD template contains –
- Introduction – It should contain Purpose, Scope, Background, References, Assumptions and constraints, document overview
- Methodology
- Functional Requirements
- Modeling Illustrations – Context, User Requirements, Data Flow Diagrams, Logical Data Model/Data Dictionary, Functional Requirements
- Other Requirements – Interface Requirements, Hardware/Software Requirements,
- Glossary
Now the use of BRD or FRD in organizations depends on the organization policies, practices followed by the project team and stakeholders. In my company client will share the BRD, based on the BRD we prepare FSD.
I hope now you understand the BRD vs FRD
BRD Vs FRD – Business Analyst Articles, Webinars
Sample BA Document TemplatesSend download link to: |
What is the difference between a BRD and FRD?
The Business Requirement Document (BRD) describes the high-level business needs whereas the Functional Requirement Document (FRD) outlines the functions required to fulfill the business need. BRD answers the question what the business wants to do whereas the FRD gives an answer to how should it be done
What is an FRD?
The functional requirements document (FRD) is a formal statement of an application’s functional requirements. It serves the same purpose as a contract. The developers agree to provide the capabilities specified. The client agrees to find the product satisfactory if it provides the capabilities specified in the FRD
What is difference between BRD and SRS?
It is obvious that BRS is the specification of the business processes and operations. Use Cases: SRS describes the interaction between the created product and the end users. It is the reason why this specification type includes use cases. … Specification sphere: SRS describes the peculiarities of the developed system
What is included in a requirements document?
Requirements documents should include these kinds of requirements: Business Requirements: Business requirements generally come from the customer of the project. They represent the product features, or what the end outputs of the project need to provide
What are two types of functional requirements?
Requirements generally fall into two types: functional and non-functional. The difference between them is fairly straightforward, nevertheless, in the this article we’ll define the two types of requirements and provide examples of each to point out more concretely the fundamental difference between them

Business Analyst , Functional Consultant, Provide Training on Business Analysis and SDLC Methodologies.